Intralaminar Lumbar Micro-Endoscopic Discectomy
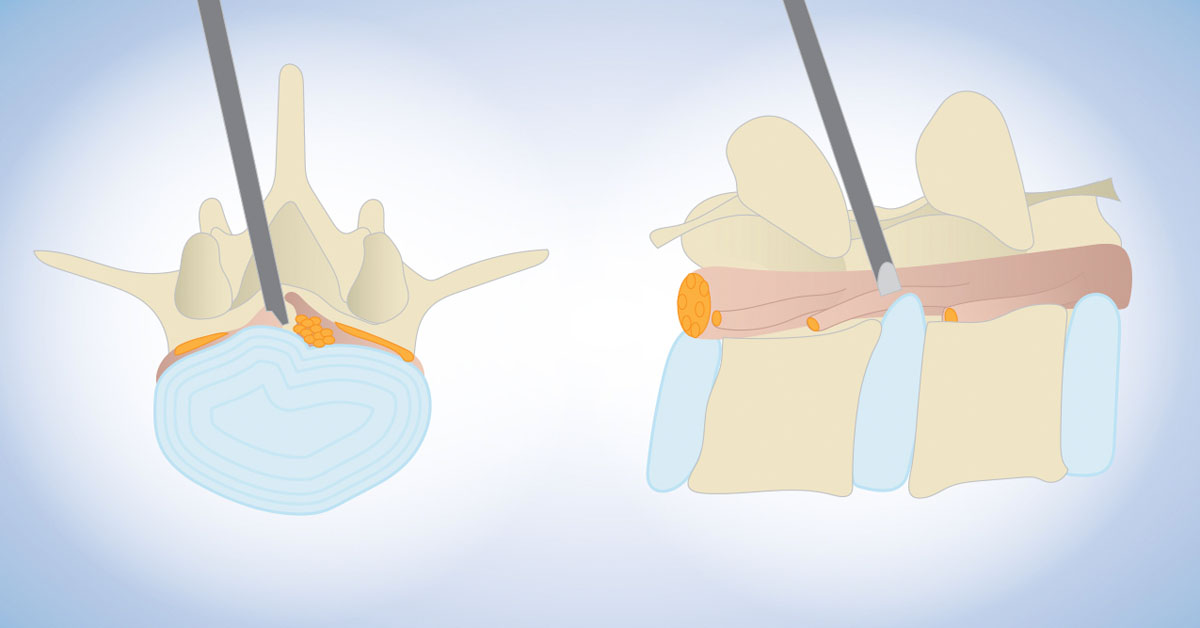
What is Intralaminar Lumbar Micro-Endoscopic Discectomy?
Intralaminar lumbar micro-endoscopic discectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is used to relieve compression on the nerve fiber causes by a herniated disc.
When is Intralaminar Lumbar Micro-Endoscopic Discectomy Performed?
This procedure is performed when degenerative changes that have affected the disc have resulted in herniation of the disc material into the spinal canal. This herniated disc can compress the nerve fiber and can cause symptoms such as pain and numbness.
The main advantage of this procedure is that it is minimally invasive meaning that open surgery is not required.
How is Intralaminar Lumbar Micro-Endoscopic Discectomy Performed?
Once consent has been obtained from the patient, the patient is laid in a face down position and administered general anaesthetic. The area of the back where the disc is herniated is cleaned with antiseptic solution. A tiny incision is made just next to the midline of the back.
Through this incision, the surgeon passes a dilator which creates a path that leads to the spinal canal. The dilator is advanced all the way to the level of the ligamentum flavum which is a protective covering that covers the back of the spinal-cord. A cannula is advanced along the dilator and once the cannula is in position, the dilator is removed. Through this cannula, the surgeon passes an endoscope which allows him or her to visualise the structures. Instruments may be passed along the endoscope to puncture the ligamentum flavum and if necessary the intervening spinal bone. Once access is obtained to the spinal canal, the nerve fiber are gently moved to the side so that the herniated disc can be visualized. With the aid of special excision devices, the herniated disc is removed and the area is sealed.
Once the surgeon is satisfied that the entire herniated disc has been removed, the instruments are taken out and a small bandage is applied over the incision. The patient is observed for a few hours and is subsequently discharged home.
Advantages and Benefits
As the surgery is minimally invasive, there is rarely any damage to the neighboring tissues. Recovery times are short and results are excellent. Patients can notice a difference in their symptoms fairly quickly.
Disadvantages and Risks
While extremely rare, risks include mild bruising at the site of the incision and mild pain which can be easily treated with painkillers. Infection risks are low as is damage to the nerve fiber.
